The U.S. industrial automation industry is experiencing a powerful renaissance in late 2025—a transformation not seen in decades. Fueled by dramatic technological advancements, a new wave of government incentives, and renewed urgency around manufacturing sovereignty, the entire sector is at the heart of what top analysts now call America’s “new profit cycle.”
This cycle is not simply a short-lived rebound from pandemic-era lows; it’s a wholesale restructuring—one that’s impacting everything from Wall Street allocations to shop floor operations. As capital floods into automation, robotics, power systems, and factory software, U.S. companies are rewriting the rules that have governed manufacturing and supply chain strategy for a generation.
This article explores the drivers of this profit renaissance:
-
Technology investments in AI, robotics, and digital controls
-
U.S. policy moves, from reshoring incentives to grid modernization
-
Structural shifts away from “growth at all costs” toward durable, cash-generating operations
-
The best-positioned industrial automation stocks for your portfolio
-
How investors can benefit from the new industrial playbook
The Foundations of America’s 2025 Automation Boom

After decades of prioritizing low-cost manufacturing overseas, the United States is witnessing a profound shift in how—and where—things are made. What’s remarkable about late 2025 is not only the scale of industrial capital flowing inward, but also the structural reasons behind it:
Labor Shortages and Wage Pressures:
With U.S. unemployment hovering near multi-decade lows, finding skilled manufacturing workers is becoming more difficult and costly. Major industrial firms are being forced to accelerate automation not just as an edge—but as a survival strategy.
Technology Investment’s Tipping Point:
Key advances in AI, sensors, robotics, and machine vision have finally moved from laboratory proofs to mass adoption. Instead of standalone robot arms, factories now integrate everything from predictive maintenance analytics to adaptive workflow optimization.
Grid Modernization, Electrification, and Sustainability:
The race to electrify America’s grid, meet tough new ESG standards, and manage rising energy costs is forcing companies to rethink every aspect of industrial design. Intelligent power management and energy-efficient automation are now essential investments.
Reshoring and National Security Concerns:
Following pandemic-era supply chain shocks and geopolitical events, U.S. policy has leaned hard into manufacturing independence. Tariffs, subsidies, and sectoral incentives are tilting the playing field back toward domestic production, especially in critical technologies.
Investor Rotation from “Asset-Lite” to Capital-Intensive Sectors:
After years where software and social media stocks dominated market gains, Wall Street is rediscovering the appeal of “heavy” sectors with defensible barriers, physical assets, and government tailwinds. As capital rotates, the automation sector finds durable support for higher valuations.
How Policy and Macroeconomics Are Accelerating Industrial Change
The current boom isn’t a classic, stimulus-only rally—it’s bigger and likely to last far longer.
Key pillars include:
Looser Federal Reserve Policy
After a prolonged cycle of tightening, the Federal Reserve has shifted posture. Lower interest rates unlock new capital expenditure budgets in sectors that had been squeezed by decades of under-investment.
Elevated Fiscal Spending
Policy waves like the Inflation Reduction Act, the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act, and the CHIPS and Science Act have together allocated over $1 trillion across the coming decade for U.S. infrastructure, clean energy, and advanced manufacturing. This public investment is not only modernizing transportation, energy, and semiconductor supply—but is also catalyzing huge private-sector capital inflows.
Reshoring Incentives Create Critical Mass
By directly subsidizing onshore plant construction, favoring U.S. sourcing, and attaching incentives to Made-in-the-USA components, federal and state governments have created a flywheel: as more supply chains localize, adjacent industries are pressured to do the same, accelerating a manufacturing “homecoming.”
From Growth at All Costs to Profitable, Resilient Operations
“There’s merit to the ‘asset-lite era’ thesis,” says Paul Holmes of BrokerListings, “but now companies with lower fixed costs can sustain above-average valuations. Today, companies with real operational leverage and durable infrastructure are best positioned to offer investors a blend of resilience and upside.”
What’s changing on-the-ground?
-
Automation as risk insurance: Companies that own their supply chain, use proprietary robotics, and develop in-house factory software can operate with greater agility, less vulnerability to labor shocks, and higher profit consistency.
-
Operational strength over hype: As Mike Fullam, CEO of Togo Supply Chain Resource Group, puts it: “Investments reduce risk and improve execution. Growth isn’t vanishing, but companies with stronger operational foundations are better positioned to scale.”
-
Necessity-driven capital expenditures: Marcello Lo Cicero of React Power Solutions notes a clear capital shift: “We’re moving from ‘growth at all costs’ to mission-critical automation, grid upgrades, and power resiliency… these projects provide steadier margins compared to ad-driven tech cycles.”
This new discipline makes automation investments less cyclical and more strategic: companies are no longer spending simply to chase growth—they are automating to survive, protect margins, and scale efficiently.
Reshoring: The Great American Manufacturing Renaissance
John Murillo, chief business officer at B2Broker, sums up the profound change: “Reshoring is real. Manufacturing construction is running at twice the 2019 pace. Labor shortages and cybersecurity needs are rapidly pulling automation demand forward.”
What’s fueling this boom?
-
Record government incentives: Over $1 trillion in new incentives and infrastructure spending.
-
Supply chain resilience: Reducing dependence on risky overseas vendors, especially in critical sectors like semiconductors, medical devices, and battery technologies.
-
Automation as an equalizer: In high-cost labor markets, automation allows U.S. factories to operate competitively, offsetting wage differentials with tech-driven productivity.
-
Cybersecurity imperatives: Domestic production reduces digital risk and creates tighter control over sensitive manufacturing flows.
Three Automation Stocks to Engineer Your Portfolio
Industrial automation has moved from a cyclical, “nice-to-have” allocation to a core, must-own sector for forward-looking investors. With Merrill Lynch calling for a sustained “new profit cycle,” three companies consistently appear at the top of sector watchlists: ABB Ltd. (ABBNY), Eaton Corp. (ETN), and Rockwell Automation (ROK).
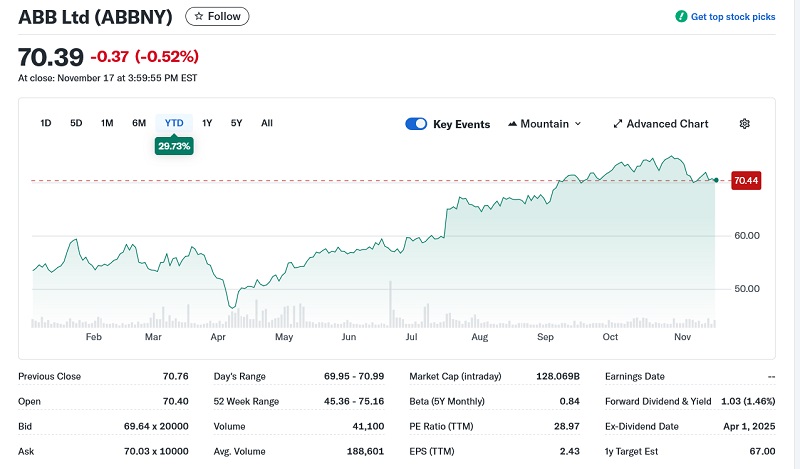
ABB Ltd. (OTCPK: ABBNY)
-
Current Share Price: $70
-
YTD Performance: +12.2%
-
Headquarters: Zurich, Switzerland
ABB delivers world-class robotics, motion control, and power management. Few companies offer such broad exposure to the dominant forces now shaping manufacturing: digitalization, data center electrification, and advanced grid infrastructure.
As Marcello Lo Cicero says, “ABB’s breadth across motion, robotics, and power management positions it well for factory automation and energy efficiency.” The company’s global leadership and deep R&D give it resilience across cycles.
Eaton Corp. (NYSE: ETN)
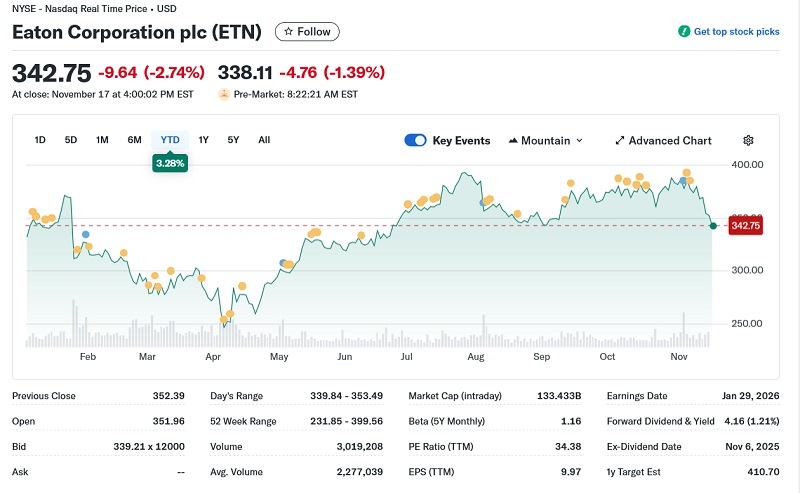
-
Current Share Price: $342
-
YTD Performance: +6.8%
-
Headquarters: Dublin, Ireland
Eaton is evolving into America’s backbone for power management and electrical infrastructure—critical as data centers, industrial facilities, and AI labs multiply across the U.S.
Paul Holmes underscores their importance: “Eaton is critical for AI data centers and reshoring facilities.” With robust dividend payouts, expanding backlog from grid upgrades, and market leadership in electrification, the stock offers both growth and income.
Rockwell Automation (NYSE: ROK)
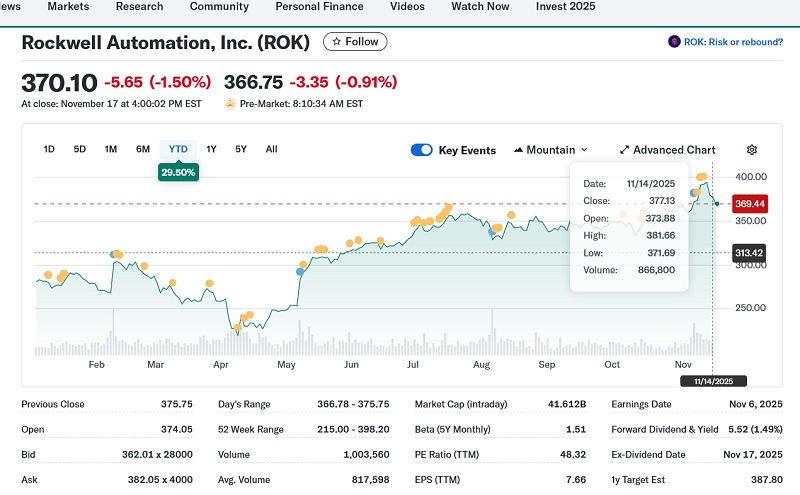
-
Current Share Price: $370
-
YTD Performance: +32.2%
-
Headquarters: Milwaukee, WI
Rockwell is America’s automation champion. Dominant in industrial AI, lifecycle services, and manufacturing software, ROK excels in operational relationships that drive stickier, higher-margin recurring revenue.
Lo Cicero notes Rockwell as “a high-mix automation leader,” and Murillo points to “intelligent devices, robotics, and industrial AI” as its growth engines. For investors, Rockwell offers targeted exposure to the brains and backbone of American reindustrialization.
Industrial Automation: A Shift from Cyclical to Structural Allocation
For decades, industrial automation was viewed as a cyclical investment—“nice to have” during expansion phases, expendable during downturns. In 2025, that paradigm is collapsing. Automation, robotics, and factory software have become strategic, structural necessities for manufacturers, supply-chain operators, and investors alike.
Why Has Industrial Automation Shifted Toward Permanence?
-
Reshoring and National Security Concerns
Recent global shocks—from pandemic disruptions to geopolitical tension—highlight the fragility of extended supply chains. U.S. policy response has emphasized domestic capacity, and automation is pivotal for making domestic plants cost-effective, flexible, and resilient. -
Labor Shortages Create Permanent Demand
As Baby Boomers retire and immigration flows tighten, U.S. manufacturers face an enduring shortage of skilled workers. Automation does not just solve temporary bottlenecks; it is the only sustainable solution for maintaining throughput. -
Grid Upgrades and Electrification Pressures
With clean energy and electrification now national priorities, companies must modernize facilities for digital controls, smart power, and real-time monitoring. Legacy assets without robust automation are being eclipsed. -
Massive Federal Incentives = Long-lasting Investment Flows
Trillions in public funding have created a foundational market for industrial tech, giving companies visibility and confidence to invest across cycles.
What Does This Mean for Investors?
Sector allocation models are changing. Professional portfolio managers are moving toward structural, core exposure in automation and factory software—placing it alongside classic defensives like consumer staples and utilities, but with far higher medium-term growth.
“From a supply chain perspective, Merrill Lynch’s new profit cycle is logical,” says Mike Fullam, CEO at Togo Supply Chain Resource Group. “Industrial automation creates repeatable, measurable profit opportunities by curbing risk and gaining better business outcomes.”
The End of “Just in Time” — Automation Enables Robustness
For years, manufacturing aimed for maximum efficiency—minimal inventory, tight supplier networks, and relentless cost-cutting. While successful in stable times, this left companies exposed to disruption. Today, automated plants and digital controls allow for greater operational robustness, adaptability, and higher long-term returns.
Factory Software, Robotics, and Next-Gen Grid Upgrades
The pillars of advanced automation extend beyond traditional robotics arms. The sector now integrates a constellation of digital technologies, each indispensable for modern U.S. manufacturing.
Factory Software Ecosystems
Modern manufacturing is driven by software as much as hardware. Leading plants deploy entire ecosystems of tools:
-
MES Platforms (Manufacturing Execution Systems):
Track production, inventory, and workflow in real-time, enabling quick pivots in demand, supply, or process—from food and pharma to automotive and microchips. -
Predictive Maintenance and AI Analytics:
IoT sensors and AI models predict machine failure before it happens, slashing downtime and maintenance costs. -
Adaptive Workflow Automation:
Software optimizes human/robot coordination, energy use, logistics, quality assurance, and compliance.
Robotics Revolution
Robotics have become the backbone of American competitiveness. New categories include:
-
Collaborative Robots (“Cobots”):
Work alongside humans, handling dangerous, tedious, or precision tasks. -
Flexible Automation:
Systems that can be rapidly reconfigured for new products or processes, busting the myth of “dumb” factory lines. -
Vision-Based QC and Precision Materials Handling:
Automated inspection and specialty robotics increase consistency and reduce waste.
Grid and Energy Management Innovation
The clean energy wave is forcing industrial facilities to rethink their entire power landscape. Advances include:
-
Smart Grid Interfaces:
Synchronize plant energy demand with volatile supply, supporting renewables and removing grid bottlenecks. -
EV Charging Infrastructure:
As electric vehicles scale, plants and logistics hubs need rapid, flexible charging installations—integrated into broader workflow automation for efficiency. -
Power Resilience Solutions:
Battery storage systems, microgrids, and intelligent switching reduce downtime and guard against cyber and weather risk.
Data Center Electrification
Manufacturing is not just physical—it’s increasingly digital. As automation drives up data processing requirements, demand for “hyperscale” data centers is booming. Companies like ABB and Eaton are core suppliers to these facilities, providing everything from heat management systems to resilient backup power.
Labor Shortages, Talent Gaps, and the Automation Imperative
The U.S. labor market for skilled manufacturing is tight—and trending tighter. According to the National Association of Manufacturers, there are over 700,000 unfilled U.S. manufacturing jobs in late 2025. Wage inflation, an aging workforce, and competition for high-tech talent make automation the only feasible way for many plants to survive and scale.
Demographics: The Skills Squeeze
-
Retirement of Skilled Workers:
Manufacturing’s skilled labor pool is shrinking as experienced technicians retire. Training new workers is expensive and slow; automation bridges the gap. -
Education System Misalignment:
U.S. STEM programs have not kept pace with advanced manufacturing needs—AI, cloud-systems, and robotics expertise is at a premium. -
Immigration Constraints:
Tighter U.S. immigration policies in recent years have further reduced the availability of incoming manufacturing workers.
Automation as Equity
For many companies, automation isn’t a luxury—it’s a form of equity protection. Plants that automate are less exposed to labor cost shocks, strikes, or demographic risk. They can scale output without linear scaling in headcount, preserving margins and gaining pricing power in tight markets.
Mike Fullam observes: “Investments in industrial automation create repeatable, measurable profit opportunities by gaining operational leverage and reducing human resource risk. The companies best able to adapt will win the next decade.”
Federal Incentives: Trillions Fueling Industrial Capacity

The full force of government action is now behind America’s industrial acceleration. Unlike previous cycles that oscillated with short-lived tax holidays or regulatory tweaks, 2025’s program represents long-term, predictable funding.
Key Federal Programs Driving Automation
-
Inflation Reduction Act (IRA):
Funding flows to clean energy manufacturing, grid modernization, and domestic sourcing for renewable supply chains. -
Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (IIJA):
Supports modernized transit, digital controls, upgraded water and power distribution—all sectors dependent on advanced automation and controls. -
CHIPS and Science Act:
Direct incentives for new semiconductor manufacturing facilities and associated supply chain technology. -
Advanced Manufacturing Credits and R&D Deductions:
Companies deploying next-gen automation systems gain bonus credits and deductions, further amplifying investment appetite.
John Murillo notes: “Cash is a powerful market incentive. With over a trillion dollars in incentives, industrial order books are full. Reshoring is not just a talking point—it’s visible in hundreds of new facilities across the country.”
The Private Sector’s Response
Rather than simply pocketing subsidies, companies are leveraging public funds as co-investment. For every billion in government allocation, private industry is pledging billions more—often at rates that multiply the effect.
Backlog statistics for industrial tech vendors confirm a golden era: ABB, Eaton, Rockwell, and their peers report record forward order books, expanded manufacturing footprints, and new client wins in sectors from auto to AI hardware to infrastructure logistics.
Infrastructure Build-Outs: Electrification, AI, and Power Management
America’s infrastructure spending spree is not just about new highways; it’s about building a digital, energy-smart foundation for the next century of manufacturing prowess.
Electrification Everywhere
-
Factories and Warehouses:
To compete globally, U.S. facilities are ramping up energy efficiency, digitizing controls, and integrating renewable sources. -
Data Centers:
Supporting the AI revolution, hyperscale data centers demand advanced cooling, backup generation, and automation for smooth operation. -
EV Charging Networks:
Widespread adoption of electric fleets requires thousands of charging stations, software management tools, and grid-to-device integration.
Automation Is the Backbone
Rockwell Automation’s partnerships illustrate the new era: through tight integration of operational data, process control, and predictive maintenance, automated plants can achieve record efficiency, lower cumulative downtime, and virtually eliminate obsolete inventory.
Marcello Lo Cicero explains: “Capex is shifting from ‘growth at all costs’ to mission-critical automation, grid upgrades, and power resiliency. These projects provide steadier margins—and true operational durability—compared to ad-driven tech cycles.”
“Smart” Power Management As Core Competency
Eaton, ABB, and other automation giants are rapidly becoming the digital “brains” of U.S. infrastructure. Their software-driven power management platforms support:
-
Factory-level load balancing
-
Energy cost optimization and carbon tracking
-
Grid-response automation for surge protection and renewable integration
-
Secure, scalable cybersecurity for mission-critical systems
Paul Holmes puts it simply: “Electrification exposure, pricing power, and operational resilience—these are the real drivers for 2025–2026 market performance. Companies supplying these solutions are critical not just for industry, but for the nation’s strategic interests.”
Case Studies: Automation Success Stories Across U.S. Industry
To truly grasp the transformation underway in U.S. industrial automation, it’s critical to see it in real-world operations. These case studies shine a light on the strategies, results, and lessons learned by companies leading the 2025 profit cycle.
An Automotive Giant Reinvents Its Factory with Smart Automation
In the Midwest, a major U.S. auto manufacturer faced mounting costs and delays as it attempted to reshore electric vehicle production. Labor shortages, unpredictable supply chains, and rising energy costs threatened margins. Management embarked on a multi-year investment in ABB robotics and Rockwell factory software to transform its flagship plant.
Key elements:
-
Deployment of collaborative robots (cobots) to work with human teams on battery and drivetrain assembly
-
Advanced sensors linked to predictive maintenance algorithms, reducing unplanned downtime by 40%
-
Integration of Eaton’s smart power management for grid responsiveness and energy cost savings
Results:
In two years, the factory achieved a 28% increase in throughput, a 35% reduction in defect rates, and reached energy efficiency targets three years ahead of Corporate ESG deadlines. The facility now serves as a template for the brand’s reshoring and electrification plans.
Food Processing Leader Gains Reliability Through Automation
A national food processor, dealing with hygiene mandates and an aging plant workforce, joined forces with ABB for end-to-end automation of its packing lines.
Key strategies:
-
Machine vision quality controls enable real-time surface inspection, eliminating manual visual checks
-
AI-driven workflow scheduling aligns production with variable raw material supplies
-
Scalable Rockwell MES (Manufacturing Execution System) allowed rapid adaptation during seasonal demand spikes
Results:
The processor slashed labor costs by 22%, cut food waste by 15% due to higher precision, and reduced product recalls with improved consistency. This success spurred new public-private partnerships for modernizing America’s food infrastructure.
Data Center Operator Secures a Competitive Edge
A leading U.S. data center company, supporting both traditional cloud and AI computing workloads, partnered with Eaton to overhaul its facilities for never-fail reliability.
Highlights:
-
Microgrid integration for backup power and renewable energy optimization
-
Eaton’s cybersecurity-enhanced digital controls guard against ransomware and grid hacks
-
Rockwell’s power utilization software sharpens energy forecasting and peak usage billing
Results:
The data center achieved a 99.995% uptime rating (industry-leading), reduced annual power purchasing costs by 12%, and won new contracts from tech unicorns seeking “always-on” computing.
Risks and Headwinds: What Investors Should Watch
While the outlook for U.S. industrial automation is robust, prudent investors recognize that no trend is without risk. Understanding the sector’s headwinds is vital for risk management and realistic return projections.
Economic Slowdowns and Interest Rate Risk
-
Cyclical Sensitivity:
Although the sector is more structural than ever, large-scale automation investments are still partially tied to broad economic growth and capital availability. A sharp recession or unexpected rate hikes could slow new orders, even as backlog cushions near-term results. -
Policy Shifts:
Major incentives underpinning the current boom are subject to change with elections and fiscal priorities. Changes could impact subsidy flows and project timelines, especially if a future administration cuts industrial or clean energy budgets.
Technology Implementation and Integration Challenges
-
Talent Scarcity:
The biggest limiting factor for companies rolling out advanced robotics is often a shortage of software engineers, integrators, and AI specialists. Prolonged talent gaps can lead to project delays or underutilization of installed technologies. -
Cybersecurity:
Digitally integrated factories and infrastructure are attractive targets for hackers. Without robust, multilayered defenses, automation can become a liability. Companies must continually update protocols, invest in staff training, and prepare for evolving threats.
Supply Chain Disruptions and Geopolitical Risks
-
Component Sourcing:
Even with reshoring, many automation components (microchips, specialty sensors, etc.) are globally sourced. Broader geopolitical shocks, trade disputes, or recurring pandemics could cause component delays and cost escalations. -
Fragmentation and Standards:
The accelerating innovation race risks creating a patchwork of platforms and integration headaches. Companies relying on legacy automation platforms may struggle to upgrade or interconnect with newer tech.
Valuation Concerns
-
Stock Price Appreciation:
Some automation leaders have experienced rapid share price increases, raising concerns about potential overvaluation. Investors must assess not just growth but the durability of competitive advantages and margin expansion. -
Overreliance on Incentives:
Firms most exposed to government contracts or one-off subsidies could see near-term momentum fade if policies change, so careful due diligence on backlog quality is essential.
Portfolio Strategy: Allocating to the New Industrial Cycle

Given the scale and durability of the 2025 automation boom, investors are actively recalibrating their portfolios. Here’s how strategic allocation is evolving, and what characteristics define the most attractive investment candidates.
Why Industrial Automation Deserves a Core Allocation
Industrial automation is no longer a tactical or niche bet. The current environment strongly supports making automation stocks a core, long-term holding for growth, income, and inflation protection.
Portfolio benefits:
-
Exposure to vital, government-backed secular trends
-
Favourable risk/reward compared to more cyclical industrial bets
-
Resilience to labor, energy, and supply shocks
-
Dividend opportunities, especially among established players like Eaton and ABB
-
Portfolio diversification away from “asset-lite” tech, providing a hedge against digital ad or SaaS slowdowns
Building a Balanced Automation Portfolio
Here are recommended strategies for different investor risk profiles:
Long-term Growth Investors
-
Prioritize pure-plays with high R&D spending, global leadership in robotics, and heavy exposure to next-gen factories (e.g., Rockwell Automation)
-
Allocate a core weighting to diversified solution providers with recurring software revenue streams
-
Consider thematic ETFs tracking U.S. industrial automation and reshoring indexes
Income and Defensive Investors
-
Focus on established multi-industrial companies (e.g., Eaton, ABB) with broad government contract exposure, strong dividends, and solid backlogs
-
Mix with utility or infrastructure names that benefit from grid modernization, electrification, and resilient power management
Thematic Tactical Investors
-
Seek exposure to firms benefiting most from AI integration, cybersecurity, and “smart” grid build-outs
-
Rotate between automation verticals (factory software, sensors, robotics, EV infrastructure) as cyclical conditions change
-
Use options or sector ETFs for risk-managed plays on earnings, contract wins, or regulatory news
Timing and Entry Points
While automation stock prices reflect much of the positive secular narrative, near-term volatility—driven by macro policy, interest rates, or geopolitics—can create attractive entry points. Investors should:
-
Monitor quarterly earnings for backlog growth, contract wins, and pricing power signals
-
Watch for sector pullbacks tied to “macro noise”; these dips are often transitory in powerful secular bull cycles
-
Rebalance to maintain strategic weightings as automation allocation grows in overall portfolio value
Long-Term Outlook: How “Smart” Manufacturing Is Securing America’s Future
The case for persistently higher investment in U.S. industrial automation does not hinge on a single cycle, electoral outcome, or headline. The deep secular tailwinds reshaping American manufacturing are poised to drive growth and margin expansion for years to come.
Labor, Demographics, and Competitiveness
-
The U.S. will continue to face an aging workforce and skills mismatches, ensuring long-term demand for factory automation
-
Reshoring and “friendshoring” strategies reduce geopolitical risk, bringing more high-value, tech-driven manufacturing back to American soil
-
Sustained government funding, combined with private sector innovation, will make the U.S. among the leaders in smart, energy-efficient production
Tech Innovation and Platform Economics
-
AI, cloud-connected controls, 5G/6G integration, and quantum computing will make future factories even more adaptive, resilient, and productive
-
Software platforms and recurring revenue streams are turning many traditional automation firms into “digital” companies, with higher valuation multiples and customer stickiness
Global Supply Chains, Geopolitics, and Security
-
American automation companies will play a leading role in rebuilding critical supply chains—not just domestically, but in allied and friendly nations seeking alternatives to risky regions
-
Cybersecurity will become a central pillar of factory design, with dedicated teams and integrations from the earliest stages of plant planning
ESG and Environmental Leadership
-
With climate and resource mandates intensifying, sustainable manufacturing will rely on automation to optimize energy use, minimize materials waste, and streamline carbon tracking and reporting
-
Automation enables adaptive resource management—providing live feedback on sustainability targets.
Final Thoughts: The New Era of Profitable Industrial Innovation
Industrial automation’s momentum is not a passing phase—it is the backbone of America’s next industrial “golden era.” By combining traditional strengths in engineering and innovation with advanced software, AI, and resilient supply strategies, the United States is poised for a wave of sustainable, profitable growth unlike anything seen since the mid-20th century.
Key takeaways for executives and investors:
-
The sector’s new “profit cycle” is grounded in fundamentals—structural demand, capital inflows, and government support
-
Factory software, robotics, and smart grid upgrades represent powerful, diversified growth themes
-
Leaders like ABB, Eaton, and Rockwell are poised to capture multi-year tailwinds, providing both stability and upside
-
Risks remain, from policy shifts to cyber threats, but the secular case is compelling and enduring
-
The time is right to make industrial automation a core allocation, benefiting from the sector’s central role in rebuilding and modernizing U.S. economic and industrial power
By staying ahead of these trends—through research, portfolio discipline, and strategic investment—today’s content creators and investors can position themselves at the crossroads of innovation, policy, and secure, sustainable profitability.
Frequently Asked Questions: U.S. Industrial Automation & Investing
<!– wp:wpseopress/faq-block-v2 {"schema":{"@context":"https://schema.org","@type":"FAQPage","url":"https://steadyincomeinvestments.com/top-3-industrial-automation-stocks-to-consider-for-2026/","@id":"https://steadyincomeinvestments.com/top-3-industrial-automation-stocks-to-consider-for-2026/","mainEntity":[{"@type":"Question","url":"https://steadyincomeinvestments.com/top-3-industrial-automation-stocks-to-consider-for-2026/#why-is-the-u-s-industrial-automation-sector-booming-in-2025","name":"Why is the U.S. industrial automation sector booming in 2025?","answerCount":1,"acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"\u003cp\u003eThe U.S. industrial automation sector is booming due to a combination of labor shortages, government infrastructure incentives, advances in AI and robotics, supply chain reshoring, and a pivot toward operational resilience over speculative growth. Massive federal investments and the need for smarter, more efficient factories have created a structural, multi-year profit cycle across the automation industry.\u003c/p\u003e"}},{"@type":"Question","url":"https://steadyincomeinvestments.com/top-3-industrial-automation-stocks-to-consider-for-2026/#what-are-the-best-industrial-automation-stocks-to-watch-right-now","name":"What are the best industrial automation stocks to watch right now?","answerCount":1,"acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"\u003cp\u003eLeading automation stocks to watch include ABB Ltd. (ABBNY), Eaton Corp. (ETN), and Rockwell Automation (ROK). These companies offer strong exposure to robotics, factory software, smart power management, and grid modernization, all of which are in high demand as U.S. manufacturing undergoes digital transformation.\u003c/p\u003e”}},{“@type”:”Question”,”url”:”https://steadyincomeinvestments.com/top-3-industrial-automation-stocks-to-consider-for-2026/#how-do-labor-shortages-impact-demand-for-automation”,”name”:”How do labor shortages impact demand for automation?”,”answerCount”:1,”acceptedAnswer”:{“@type”:”Answer”,”text”:”\u003cp\u003eLabor shortages in U.S. manufacturing are a key driver for investment in automation technology. With fewer skilled workers available and wage costs rising, companies are increasingly relying on robotics, smart systems, and factory software to maintain output, improve quality, and preserve margins.\u003c/p\u003e”}},{“@type”:”Question”,”url”:”https://steadyincomeinvestments.com/top-3-industrial-automation-stocks-to-consider-for-2026/#what-role-do-government-incentives-play-in-the-industrial-automation-boom”,”name”:”What role do government incentives play in the industrial automation boom?”,”answerCount”:1,”acceptedAnswer”:{“@type”:”Answer”,”text”:”\u003cp\u003eFederal and state incentives—such as those from the Inflation Reduction Act and major infrastructure bills—are providing substantial funding for industrial modernization, grid upgrades, and clean energy projects. These incentives lower the cost of advanced automation systems, accelerate plant investments, and underpin rising order backlogs at leading automation companies.\u003c/p\u003e”}},{“@type”:”Question”,”url”:”https://steadyincomeinvestments.com/top-3-industrial-automation-stocks-to-consider-for-2026/#is-industrial-automation-a-cyclical-or-structural-investment-trend”,”name”:”Is industrial automation a cyclical or structural investment trend?”,”answerCount”:1,”acceptedAnswer”:{“@type”:”Answer”,”text”:”\u003cp\u003eWhile traditionally viewed as cyclical, industrial automation is now seen as a structural growth trend. Robust government support, secular labor issues, digital transformation requirements, and persistent supply chain risks mean automation spending is expected to continue regardless of short-term economic cycles.\u003c/p\u003e”}},{“@type”:”Question”,”url”:”https://steadyincomeinvestments.com/top-3-industrial-automation-stocks-to-consider-for-2026/#what-are-the-major-risks-to-automation-investments-in-2025-and-beyond”,”name”:”What are the major risks to automation investments in 2025 and beyond?”,”answerCount”:1,”acceptedAnswer”:{“@type”:”Answer”,”text”:”\u003cp\u003eKey risks include economic slowdowns, shifts in fiscal policy, supply chain disruptions for high-tech components, talent shortages in automation engineering, and cybersecurity threats to digitally integrated factories. Thorough due diligence and portfolio diversification can help mitigate these risks.\u003c/p\u003e”}},{“@type”:”Question”,”url”:”https://steadyincomeinvestments.com/top-3-industrial-automation-stocks-to-consider-for-2026/#how-does-automation-improve-supply-chain-resilience”,”name”:”How does automation improve supply chain resilience?”,”answerCount”:1,”acceptedAnswer”:{“@type”:”Answer”,”text”:”\u003cp\u003eAutomation enhances supply chain resilience by reducing reliance on human labor, enabling real-time data-driven decisions, supporting flexible manufacturing, and protecting operations from disruptions such as strikes or pandemics. Smart systems also improve inventory management and logistics efficiency.\u003c/p\u003e”}},{“@type”:”Question”,”url”:”https://steadyincomeinvestments.com/top-3-industrial-automation-stocks-to-consider-for-2026/#can-small-and-midsize-manufacturers-benefit-from-automation-or-is-it-just-for-large-corporations”,”name”:”Can small and midsize manufacturers benefit from automation, or is it just for large corporations?”,”answerCount”:1,”acceptedAnswer”:{“@type”:”Answer”,”text”:”\u003cp\u003eBoth large corporations and small/midsize manufacturers can benefit from automation. Scalable robotics, cloud-based factory software, and financing incentives have made advanced automation solutions more accessible and cost-effective than ever before, enabling even smaller firms to modernize operations.\u003c/p\u003e”}},{“@type”:”Question”,”url”:”https://steadyincomeinvestments.com/top-3-industrial-automation-stocks-to-consider-for-2026/#how-does-industrial-automation-contribute-to-environmental-sustainability”,”name”:”How does industrial automation contribute to environmental sustainability?”,”answerCount”:1,”acceptedAnswer”:{“@type”:”Answer”,”text”:”\u003cp\u003eAutomation supports sustainability by optimizing energy use, minimizing waste, ensuring consistent product quality, and enabling real-time emissions monitoring. Smart factory systems can automatically adapt production to meet resource and carbon reduction targets, supporting both ESG goals and regulatory compliance.\u003c/p\u003e”}},{“@type”:”Question”,”url”:”https://steadyincomeinvestments.com/top-3-industrial-automation-stocks-to-consider-for-2026/#what-are-the-top-future-trends-in-u-s-industrial-automation”,”name”:”What are the top future trends in U.S. industrial automation?”,”answerCount”:1,”acceptedAnswer”:{“@type”:”Answer”,”text”:”\u003cp\u003eKey future trends include:\u003c/p\u003e\u003cul class=\u0022wp-block-list\u0022\u003e\u003c!\u002d\u002d wp:list-item \u002d\u002d\u003e\n\u003cli\u003eGrowth in “smart” grid technologies and data center automation\u003c/li\u003e\n\u003c!\u002d\u002d /wp:list-item \u002d\u002d\u003e\u003c/ul\u003e\u003cul class=\u0022wp-block-list\u0022\u003e\u003c!\u002d\u002d wp:list-item \u002d\u002d\u003e\n\u003cli\u003eGreater integration of AI and machine learning for predictive maintenance\u003c/li\u003e\n\u003c!\u002d\u002d /wp:list-item \u002d\u002d\u003e\u003c/ul\u003e\u003cul class=\u0022wp-block-list\u0022\u003e\u003c!\u002d\u002d wp:list-item \u002d\u002d\u003e\n\u003cli\u003eExpansion of robotics into new industries and warehouse automation\u003c/li\u003e\n\u003c!\u002d\u002d /wp:list-item \u002d\u002d\u003e\u003c/ul\u003e\u003cul class=\u0022wp-block-list\u0022\u003e\u003c!\u002d\u002d wp:list-item \u002d\u002d\u003e\n\u003cli\u003eWidespread adoption of digital twins and industrial IoT\u003c/li\u003e\n\u003c!\u002d\u002d /wp:list-item \u002d\u002d\u003e\u003c/ul\u003e\u003cul class=\u0022wp-block-list\u0022\u003e\u003c!\u002d\u002d wp:list-item \u002d\u002d\u003e\n\u003cli\u003eCybersecurity becoming a central design pillar\u003c/li\u003e\n\u003c!\u002d\u002d /wp:list-item \u002d\u002d\u003e\u003c/ul\u003e”}}]}} –>Why is the U.S. industrial automation sector booming in 2025?
The U.S. industrial automation sector is booming due to a combination of labor shortages, government infrastructure incentives, advances in AI and robotics, supply chain reshoring, and a pivot toward operational resilience over speculative growth. Massive federal investments and the need for smarter, more efficient factories have created a structural, multi-year profit cycle across the automation industry.
What are the best industrial automation stocks to watch right now?
Leading automation stocks to watch include ABB Ltd. (ABBNY), Eaton Corp. (ETN), and Rockwell Automation (ROK). These companies offer strong exposure to robotics, factory software, smart power management, and grid modernization, all of which are in high demand as U.S. manufacturing undergoes digital transformation.
How do labor shortages impact demand for automation?
Labor shortages in U.S. manufacturing are a key driver for investment in automation technology. With fewer skilled workers available and wage costs rising, companies are increasingly relying on robotics, smart systems, and factory software to maintain output, improve quality, and preserve margins.
What role do government incentives play in the industrial automation boom?
Federal and state incentives—such as those from the Inflation Reduction Act and major infrastructure bills—are providing substantial funding for industrial modernization, grid upgrades, and clean energy projects. These incentives lower the cost of advanced automation systems, accelerate plant investments, and underpin rising order backlogs at leading automation companies.
Is industrial automation a cyclical or structural investment trend?
While traditionally viewed as cyclical, industrial automation is now seen as a structural growth trend. Robust government support, secular labor issues, digital transformation requirements, and persistent supply chain risks mean automation spending is expected to continue regardless of short-term economic cycles.
What are the major risks to automation investments in 2025 and beyond?
Key risks include economic slowdowns, shifts in fiscal policy, supply chain disruptions for high-tech components, talent shortages in automation engineering, and cybersecurity threats to digitally integrated factories. Thorough due diligence and portfolio diversification can help mitigate these risks.
How does automation improve supply chain resilience?
Automation enhances supply chain resilience by reducing reliance on human labor, enabling real-time data-driven decisions, supporting flexible manufacturing, and protecting operations from disruptions such as strikes or pandemics. Smart systems also improve inventory management and logistics efficiency.
Can small and midsize manufacturers benefit from automation, or is it just for large corporations?
Both large corporations and small/midsize manufacturers can benefit from automation. Scalable robotics, cloud-based factory software, and financing incentives have made advanced automation solutions more accessible and cost-effective than ever before, enabling even smaller firms to modernize operations.
How does industrial automation contribute to environmental sustainability?
Automation supports sustainability by optimizing energy use, minimizing waste, ensuring consistent product quality, and enabling real-time emissions monitoring. Smart factory systems can automatically adapt production to meet resource and carbon reduction targets, supporting both ESG goals and regulatory compliance.
What are the top future trends in U.S. industrial automation?
Key future trends include:
- Growth in “smart” grid technologies and data center automation
- Greater integration of AI and machine learning for predictive maintenance
- Expansion of robotics into new industries and warehouse automation
- Widespread adoption of digital twins and industrial IoT
- Cybersecurity becoming a central design pillar